Plenum Explained: Beijing to Bolster Industrial Chains, Promote Private Sector
Listen to the full version
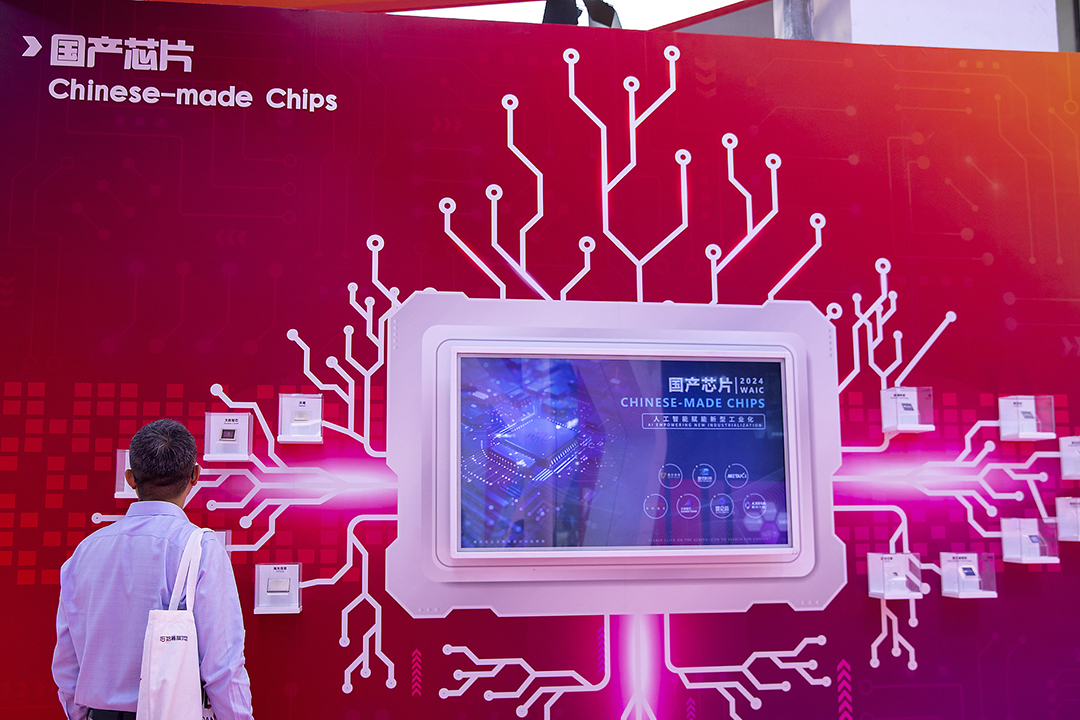

China’s top leadership has revealed a plan to deepen reforms to boost foreign trade, promote the private economy and bolster the security of the country’s industrial and supply chains, following a key political gathering.
The Communist Party of China’s Central Committee adopted the resolution at its Third Plenum — a twice-a-decade meeting of committee members that sets out China’s reform framework for the next five years — which concluded Thursday in Beijing.
Download our app to receive breaking news alerts and read the news on the go.
Get our weekly free Must-Read newsletter.
- DIGEST HUB
- China’s recently adopted reform plan aims to boost foreign trade, promote the private economy, and strengthen industrial and supply chain security.
- Measures include attracting foreign investment, increasing support for private businesses, and deepening state-owned enterprise reforms.
- The plan addresses challenges like technological restrictions from the U.S. and the EU, and aims to enhance the resilience of China's industrial sector amid economic slowdown.
China’s top leadership unveiled a comprehensive plan aimed at deepening reforms to boost foreign trade, promote the private economy, and enhance the security of the nation’s industrial and supply chains, following the Communist Party of China’s Central Committee Third Plenum. This pivotal political gathering occurs twice a decade and establishes the country’s reform framework for the subsequent five years. The resolution from the plenum includes strategies to attract fresh foreign investments and set both private and state-owned sectors on an equal footing, especially at a time when China’s economy is experiencing a slowdown due to weak domestic demand and a prolonged real estate slump [para. 1][para. 2][para. 3].
One significant focus of the resolution is securing industrial and supply chains, pledging to expedite the construction of self-supporting and risk-controllable industrial and supply chains. Specific measures include bolstering key industrial chains like integrated circuits, industrial software, and advanced materials, relocating industries domestically, and refining systems related to strategic mineral resources. This focus is due to the escalating tech rivalry with the U.S., which has imposed stricter trade restrictions on China to limit its access to advanced technology. The industrial sector is a crucial pillar of China’s economy, contributing 31.7% of the GDP or roughly 39.9 trillion yuan ($5.5 trillion) last year. However, prominent shortcomings in areas like core technology and industrial infrastructure capacity still persist, highlighting the need for ongoing reforms [para. 3][para. 4][para. 5][para. 6].
The resolution also aims to deepen foreign trade and investment reforms by developing new regulatory approaches for customs clearance, taxation, and foreign exchange, controlling trade risks, and refining the export control framework. Additionally, it seeks to upgrade pilot free trade zones, accelerate the development of the Hainan Free Trade Port, and ease restrictions for foreign investment in the manufacturing sector. Such measures signal China’s intention to expand its high-level opening to the world, especially as net foreign direct investment plummeted to a 23-year low last year. These steps are meant to bolster confidence in China’s economic prospects and ensure equal support for both domestic and foreign-funded enterprises [para. 7][para. 8][para. 9][para. 10][para. 11].
The reform of state-owned enterprises (SOEs) is another critical part of the plan, calling for deepening reforms, improving management and oversight systems, and implementing value-added accounting. State capital will focus on industries crucial to national security and the economy’s lifeblood, public services, emergency response, public welfare, and forward-looking strategic industries such as AI, aerospace, and new energy. The aim is to support the equal competition of SOEs and privately owned companies. The traditional assessment system for SOEs will be replaced by a more tailored evaluation system that includes financial performance, market competitiveness, innovation capabilities, and social responsibility [para. 12][para. 13][para. 14][para. 15].
Furthermore, the resolution underscores support for private businesses by formulating a private sector promotion law, breaking down market access barriers, refining financing support policies, and ensuring participation in major national projects. Despite accounting for over 90% of market entities and contributing significantly to employment and GDP, private sector confidence remains low due to strict pandemic controls and regulatory crackdowns. Legislation similar to the Foreign Investment Law and State-Owned Assets of Enterprises Law is proposed to secure equal legal protections and opportunities for the private sector [para. 16][para. 17][para. 18][para. 19].
Finally, China plans to accelerate the development of a new energy system and integrate electricity generated from renewable sources into power grids. This supports China’s dual carbon goals to peak emissions by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. Experts anticipate imminent power market reforms to enhance efficiency and balance climate goals with energy security, including establishing a unified national power market system and promoting carbon emissions trading [para. 20][para. 21][para. 22][para. 23][para. 24][para. 25].
- China FAW Group Corp. Ltd.
- China FAW Group Corp. Ltd., a state-owned enterprise, was one of the earliest adopters of a new assessment system for the electric vehicle segment. The new evaluation criteria include innovation, market share, and future development potential, aimed at accelerating their foray into the new-energy vehicle sector. This reform falls under China's broader efforts to reform SOEs and promote high-quality development.
- Chongqing Changan Automobile Co. Ltd.
- Chongqing Changan Automobile Co. Ltd. is one of the three central government-administered auto SOEs in China subjected to new evaluation criteria under SASAC. The new mechanism focuses on innovation, market share, and future development potential. This aims to accelerate Changan's progress in the new-energy vehicle sector, reflecting China's broader strategy for SOE reform and economic modernization.
- Dongfeng Motor Corp. Ltd.
- Dongfeng Motor Corp. Ltd. is one of the central government-administered state-owned automobile enterprises in China and an early adopter of new evaluation criteria in the state auto sector. These criteria focus on innovation, market share, and development potential to accelerate the company's progress in the new-energy vehicle sector.
- Spring Airlines Co. Ltd.
- Spring Airlines Co. Ltd. is mentioned in the article by its chairman, Wang Yu, who spoke during the "Two Sessions." He highlighted that private businesses still face unequal treatment in resource allocation and advocated for legislation similar to the Foreign Investment Law to ensure equal legal protections and opportunities for the private sector.
- Early March 2024:
- SASAC Chairman Zhang Yuzhuo announced new evaluation criteria for the electric vehicle segment of three central government-administered auto SOEs during the 'Two Sessions.'
- Thursday, July 18, 2024:
- The Third Plenum of the Communist Party of China’s Central Committee concluded in Beijing, setting out China’s reform framework for the next five years.
- Friday, July 19, 2024:
- Vice chairman Mu Hong of China’s top political advisory body stated at a press conference that measures are being used to signal China's intent to expand its 'high-level opening' to the outside world.
- Friday, July 19, 2024:
- Han Wenxiu, deputy director of the Office of the Central Committee for Financial and Economic Affairs, emphasized the importance of supporting the development of both domestic and foreign-funded enterprises equally at a press conference.
- Sunday, July 21, 2024:
- The resolution from the Third Plenum, which includes measures to attract foreign investment and level the playing field between private and state-owned sectors, was released in full by the state-run Xinhua News Agency.
- PODCAST
- MOST POPULAR






 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google
 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook
 Sign in with 财新
Sign in with 财新